ARTICLES
- HOME
- -
- ARTICLES
The Future of Security Guarding: Adapting to Technological Advances and Changing Roles

As we navigate through the 21st century, the role of security guards is undergoing a significant transformation. The traditional image of security personnel as uniformed sentinels patrolling property is evolving, influenced by advancements in technology, shifts in societal expectations, and new security challenges.
For aspiring security professionals, understanding these changes is crucial for adapting to the future demands of the field. This article explores the emerging trends and developments shaping the future of security guarding and offers insights into how future security guards can prepare for success.
1. Embracing Technological Innovation
a. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are revolutionizing the security industry by enhancing the capabilities of surveillance systems. Modern AI-powered cameras can analyze video feeds in real time, identify suspicious activities, and even predict potential threats based on behavioral patterns. Future security guards will need to be adept at managing and interpreting data from these systems, which will become central to proactive threat detection and incident management.
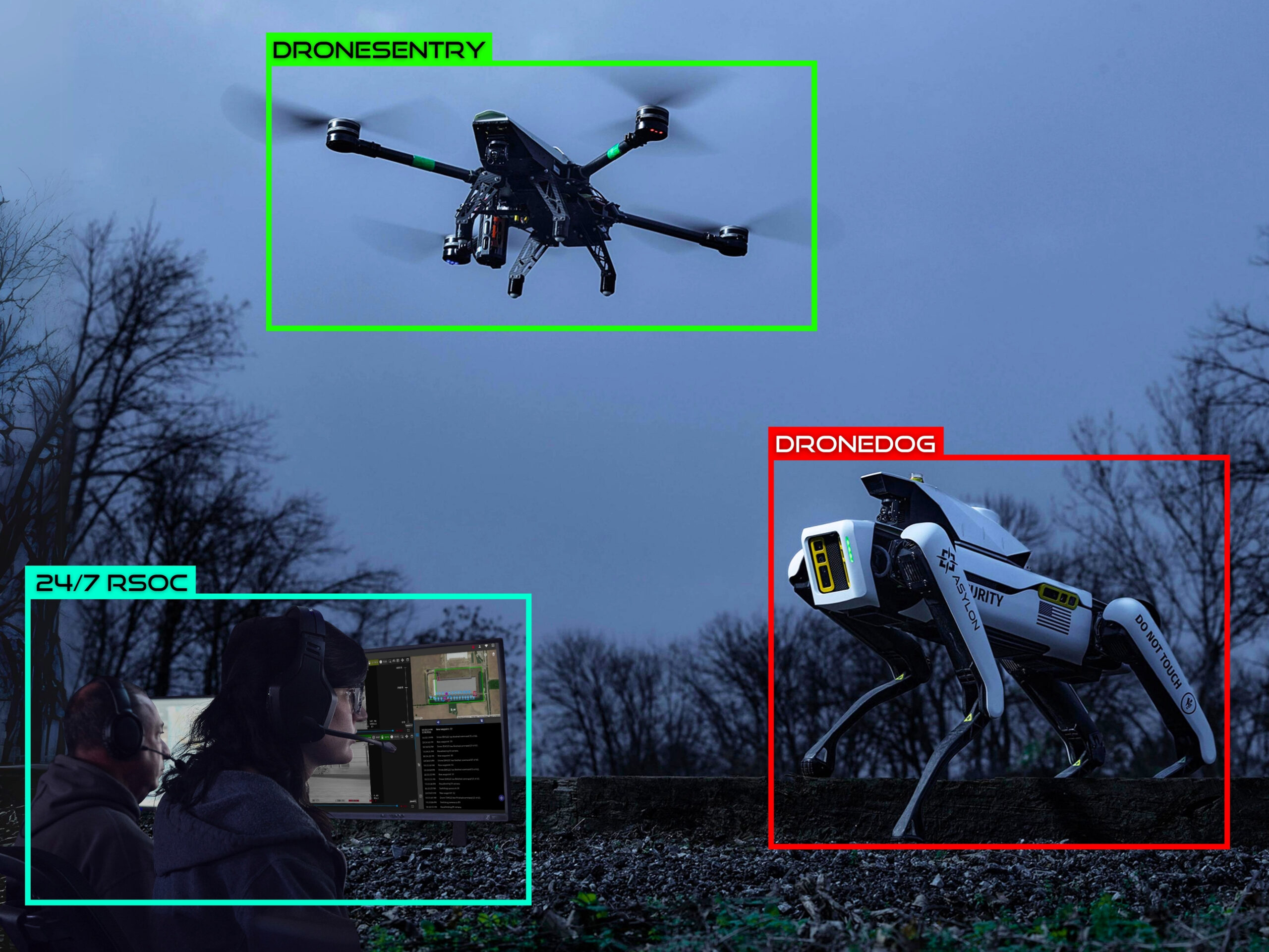
b. Drones and Robotics: Drones offer a bird’s-eye view of security operations, allowing for comprehensive surveillance of large areas and hard-to-reach locations. Meanwhile, robotics are being used for routine patrols, inspections, and even hazardous material handling. Future security professionals will need to gain expertise in operating and maintaining these technologies, as well as understanding their integration into overall security strategies.
c. Cybersecurity: As the digital realm expands, the risk of cyber threats increases. Security guards may find themselves involved in protecting digital assets and responding to cybersecurity incidents. This requires knowledge of cybersecurity principles, threat analysis, and data protection practices, alongside traditional physical security skills.
d. Internet of Things (IoT): IoT devices, such as smart sensors and connected alarms, are becoming commonplace in security systems. These devices provide real-time data and alerts about various conditions, from door breaches to environmental hazards. Security personnel will need to understand how to leverage IoT data to enhance security measures and respond effectively to alerts.
2. Developing a Diverse Skill Set
a. Technical Skills: The future security guard will need to possess a high level of technical proficiency. This includes familiarity with advanced surveillance technology, understanding the operation of drones and robots, and knowledge of cybersecurity protocols. Technical training will be essential for effectively using and maintaining these advanced systems.
b. Soft Skills: In addition to technical expertise, soft skills will play a crucial role in the future of security guarding. Effective communication, conflict resolution, and emotional intelligence will be necessary for interacting with the public, managing security teams, and handling sensitive situations with discretion.
c. Adaptability and Continuous Learning: The rapid pace of technological advancement and evolving security threats mean that continuous learning will be vital. Security guards will need to stay current with the latest industry trends, technologies, and best practices through ongoing education and professional development.
3. Shifting Responsibilities and New Roles
a. Proactive Security: The future of security guarding will increasingly focus on proactive measures rather than just reactive responses. Security personnel will be expected to conduct thorough risk assessments, implement preventive strategies, and anticipate potential threats before they escalate. This shift will require a more strategic approach to security management.
b. Customer Service Integration: As security roles become more integrated with customer service, future guards will be expected to provide assistance and support beyond traditional security duties. This could involve engaging with the public, addressing concerns, and ensuring a positive experience while maintaining security protocols.
c. Crisis Management: Future security guards will need to be skilled in crisis management, including emergency response planning, coordination with emergency services, and ensuring the safety of individuals during critical incidents. This will require a comprehensive understanding of emergency procedures and the ability to act decisively under pressure.
4. Ethical and Legal Considerations
a. Privacy and Surveillance: With the increased use of surveillance technologies, balancing security with privacy concerns will be a key challenge. Security guards will need to be aware of legal and ethical guidelines regarding data collection and privacy, ensuring that surveillance practices comply with regulations and respect individual rights.
b. Transparency and Accountability: As security operations become more complex, transparency and accountability will be essential. Security personnel will be expected to adhere to high standards of conduct, maintain accurate records, and be prepared for scrutiny from both employers and the public.
c. Ethical Use of Technology: The ethical use of advanced technologies, such as AI and drones, will be a growing concern. Future security guards will need to navigate issues related to the responsible deployment of these tools, ensuring they are used in ways that align with ethical standards and legal requirements.
5. The Path Forward
a. Education and Training: Aspiring security guards should seek out educational programs and training opportunities that cover both traditional security skills and emerging technologies. Certifications in cybersecurity, drone operation, and AI management will become increasingly valuable.
b. Networking and Professional Development: Engaging with professional organizations, attending industry conferences, and participating in networking events will help security professionals stay informed about industry developments and career opportunities.
c. Embracing Change: The ability to adapt to new technologies and evolving roles will be crucial for future security guards. Embracing change and demonstrating a willingness to learn and grow will position individuals for success in a rapidly evolving field.
Conclusion
The future of security guarding is set to be shaped by technological innovation, evolving responsibilities, and changing societal expectations. By embracing these developments, developing a diverse skill set, and navigating ethical considerations, future security guards can position themselves for success in this dynamic field. As the security landscape continues to evolve, those who are proactive, adaptable, and informed will play a critical role in safeguarding people and property in an increasingly complex world.